Tag: Heart / Stroke-Related: Coronary-Artery Disease
Adults With Coronary Artery Disease Not Meeting Cholesterol Targets
Three in four do not meet American guideline recommendations
CVD Risk Factors Predict Risk of Common Musculoskeletal Disorders
Authors found 17-fold increased risk for four or more MSDs and say findings point to need to prioritize cardiovascular health improvement
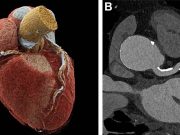
Ultrahigh-Resolution CCTA Has High Diagnostic Accuracy for Coronary Artery Disease
In a recent study, AUC of ultrahigh-resolution photon-counting coronary CT angiography was 0.93 per participant for detection of coronary artery disease
Elevated Lipoprotein(a) Predictor of Recurrent Coronary Heart Disease
Lp(a) of 500+ and 300+ mg/L versus lower significantly predicted recurrent CHD, with hazard ratios of 1.59 and 1.37, respectively
Review Compares Diagnostic Strategies for Assessment of Coronary Artery Disease
Risk for cardiovascular death and myocardial infarction similar for CCTA and ICA; risk reduced with CCTA compared with exercise ECG, SPECT-MPI
Colchicine Tied to Lower Incidence of TJA in Coronary Artery Disease
Lower incidence of total knee replacement, total hip replacement seen with use of colchicine 0.5 mg daily
Five-Year Composite Outcome Similar for TiNO-Coated Stent, Everolimus-Eluting Stents
In patients with acute coronary syndrome, decrease seen in cardiac death, MI, stent thrombosis with TiNO-coated stent, which was offset by increase in target lesion revascularization
Long-Term Outcomes Similar for Bioresorbable Vascular Scaffolds Versus Metal Stents
Increased events seen through three-year follow-up, but similar event rates observed between three and five years
Women Have About 12-Year Delay in Onset of Atherosclerosis
Women with highest atherosclerotic burden have higher risk for MACE than men, especially postmenopausal women
Poor-Quality Diet Tied to Higher Risk for Adverse CAD, PAD Outcomes
Patients with coronary artery disease or peripheral artery disease with poor diet had higher risks for major adverse cardiovascular and limb events