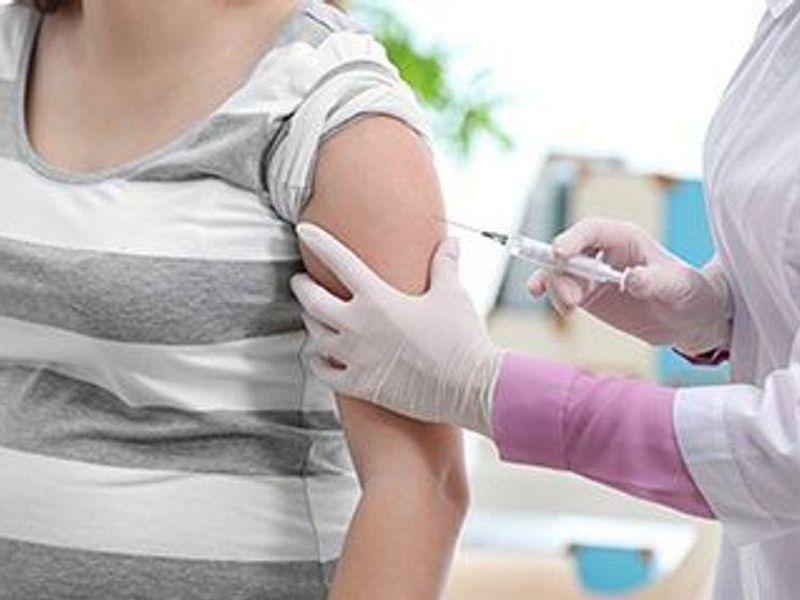
Effectiveness of maternal vaccination decreased from 70.4 percent among infants younger than 2 months to 43.3 percent in those aged 7 to 8 months
By Elana Gotkine HealthDay Reporter
TUESDAY, Oct. 10, 2023 (HealthDay News) — Maternal pertussis vaccination is associated with a reduced risk for infection among infants through 8 months of age, according to a study published online Oct. 9 in Pediatrics.
Annette K. Regan, Ph.D., from Curtin University in Perth, Australia, and colleagues conducted a population-based cohort study of 279,418 mother-infant pairs to estimate maternal vaccine effectiveness (VE) and whether maternal pertussis vaccination modifies the effectiveness of the first three infant doses of pertussis-containing vaccines.
The researchers found that pertussis was administered during 51.7 percent of pregnancies, mainly at 28 to 31 weeks of gestation. There was a decline seen in VE of maternal vaccination from 70.4 to 43.3 percent among infants younger than 2 months old versus those aged 7 to 8 months; VE was not significant after 8 months of age. Slightly lower VE point estimates were seen for the third dose of infant pertussis vaccine among maternally vaccinated versus unvaccinated infants (76.5 versus 92.9 percent), but the rates of pertussis infection were not higher.
“These results indicate that maternal pertussis vaccination protects infants from pertussis infection during a period of greatest vulnerability to severe morbidity and mortality,” the authors write. “Our findings support the infant health benefits of recommendations to administer a booster dose of pertussis vaccine near 28 weeks of gestational age.”
Copyright © 2023 HealthDay. All rights reserved.