Tag: Diabetes: Type II
ACC: More Evidence of Long-Term Benefits of Bariatric Surgery
After five years, more patients in surgery group had lower blood glucose than in medication-only group
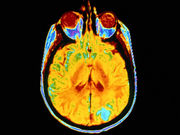
Long-Term Weight Loss Cuts Diabetes-Related Brain Changes
10-year weight loss intervention tied to lower white matter hyperintensity volume
ENDO: ‘Paleo’ Diet May Benefit Heart Health Post Menopause
Trendy eating plan may cut cholesterol, disease risks in postmenopausal women
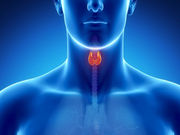
ENDO: Hypothyroidism Ups T2DM Odds Even With Low-Normal TSH
Higher free thyroxine levels associated with reduced diabetes risk
Pioglitazone Linked to Increased Risk of Bladder Cancer
Duration- and dose-response associations for pioglitazone; no correlation for rosiglitazone
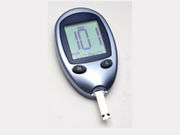
Intensive Glucose Control Offers Lasting Reduction in Risk of ESKD
In-trial reduction in risk of ESKD seen in ADVANCE trial persists after 9.9 years of follow-up
Teens With Autism More Likely to Develop Type 2 Diabetes
Additionally, those taking atypical antipsychotics showed high risk of diabetes
Off-Label Use of Metformin Common in U.S. Adolescents
Analyses of three databases show use for metabolic syndrome, PCOS, and obesity
CPAP Improves Glycemic Control in Patients With T2DM, OSA
Findings in patients with suboptimally controlled type 2 diabetes and obstructive sleep apnea
Insulin Degludec/Liraglutide Noninferior to Insulin Glargine
Fixed ratio of degludec/liraglutide superior to continued titration of glargine in uncontrolled T2DM