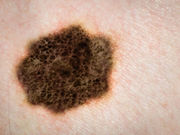
Physicians shouldn’t rely on mole count as the only reason to perform skin exams
THURSDAY, March 3, 2016 (HealthDay News) — Patients with melanoma often have few typical nevi (TN), and no atypical nevi (AN), according to a study published online March 2 in JAMA Dermatology.
Of the 566 melanoma patients in the study, 66.4 percent had zero to 20 TN in total and 73.3 percent had no AN, according to a team led by Alan Geller, M.P.H., R.N., of the Harvard School of Public Health in Boston.
The researchers found that patients younger than 60 who had more than 50 TN in total actually had a lower risk of having a thick melanoma tumor. However, patients with more than five AN were more likely to have thick melanoma than those with no AN.
Speaking in a journal news release, Geller said that the study suggests that melanomas are actually found in people with fewer moles compared to those with many moles, so doctors shouldn’t rely on mole count as “the sole reason to perform skin examinations or to determine a patient’s at-risk status.”
Copyright © 2016 HealthDay. All rights reserved.