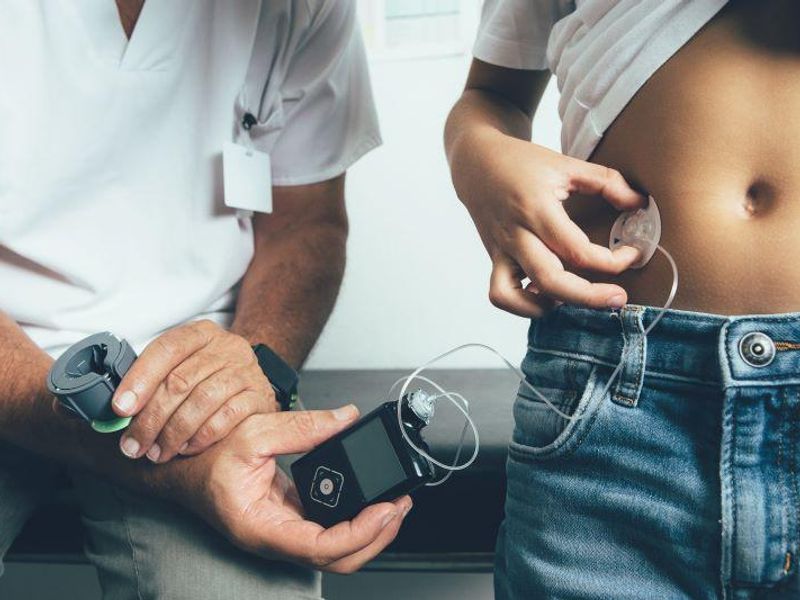
Improved glucose control seen with no increase in hypoglycemia compared with standard insulin therapy
By Elana Gotkine HealthDay Reporter
FRIDAY, Jan. 27, 2023 (HealthDay News) — For adults with type 2 diabetes, a fully closed-loop insulin delivery system improves glucose control without increasing hypoglycemia compared with standard insulin therapy, according to a study published online Jan. 11 in Nature Medicine.
Aideen B. Daly, M.B.B.S., from the Wellcome-MRC Institute of Metabolic Science at Addenbrooke’s Hospital in Cambridge, England, and colleagues conducted a randomized crossover study to compare eight weeks of the CamAPS HX fully closed-loop app with standard insulin therapy and a masked glucose sensor (control). A two- to four-week washout period separated the treatments. Twenty-eight participants were randomly assigned to two groups (14 each to closed-loop therapy first and control therapy first).
The researchers found that the proportion of time in the target glucose range (3.9 to 10.0 mmol l-1) was 66.3 ± 14.9 percent and 32.3 ± 24.7 percent with closed-loop therapy and control therapy, respectively. Time >10.0 mmol l-1 was 33.2 ± 14.8 and 67.0 ± 25.2 percent with closed-loop therapy and control therapy, respectively. Compared with the control period, mean glucose was lower during the closed-loop therapy period (9.2 ± 1.2 mmol l-1 versus 12.6 ± 3.0 mmol lâ1). In addition, hemoglobin A1c was lower following closed-loop versus control therapy (57 ± 9 mmol mol-1 versus 72 ± 13 mmol mol-1). The groups had a similar time <3.9 mmol l-1. Severe hypoglycemia events did not occur in either period.
“This study suggests that fully closed-loop insulin delivery is a safe and efficacious approach to manage type 2 diabetes in adults,” the authors write.
Dexcom supplied discounted continuous glucose monitoring devices and sensors for the study.
Copyright © 2023 HealthDay. All rights reserved.